序列化和反序列化
相信很多人都用过类的序列化和反序列化,在Android里面有Gson等第三方库可以做到,在IOS里面有setValuesForKeysWithDictionary这个方法。但是setValuesForKeysWithDictionary这个方法只能设置键值对,遇到复杂的例如Iva对象就没办法处理了。我们都知道一个实体类里面包含的数据有两类:方法和属性,其中属性又分为基本类型、容器类型和实体(对象)类型。C++里面的基本类型就那么几种:int、float、byte等。在IOS里面如果一个实体类只包含这些基本类型,那就可以通过- (void)setValuesForKeysWithDictionary:(NSDictionary<NSString *, id>; *)keyedValues;直接将一个从json字符串中提取出来的字典转为实体类,当然你必须实现-(void)setValue:(id)value forUndefinedKey:(NSString *)key方法,以防服务器返回的字段跟你实体类定义的名字不一样。
IOS中如何处理一般实体类的序列化
前面我们说Android里面有很多第三方库可以做到,IOS也是如此:Mantle、JSONModel、FastEasyMapping、MJExtension、YYModel等等。 其中我选取了YYModel作为学习对象,因为这个库文件最少最简单,而且根据他自己的介绍来看,貌似效率挺不错。
什么是id
要对一个类序列化首先需要知道IOS里面对象的结构。我们知道C里面是没有类的,只有结构体。C++在C的结构体基础上提出了类的概念和结构,OC也是如此,OC的类就是结构体。在OC里面的对象都可以使用id类型来表示,A *a也可以写成 id a。那么id是什么呢,id在objc.h中定义如下:
//A pointer to an instance of a class.
typedef struct objc_object *id;就像注释中所说的这样id是指向一个objc_object结构体的指针。objc_object在objc.h中的定义:
//Represents an instance of a class.
struct objc_object
{
Class isa;
}这个时候我们知道OBjective-C中的object在最后会被转换成C的结构体,而在这个struct中有一个isa指针,指向它的类别Class(C是大写的):
//Represents an instance of a class.
//An opaque type that represents an Objective-C class
typedef struct objc_class *Class;我们可以看到,Class本身也是指向一个C的structobjc_class:
struct objc_class
{
Class isa OBJC_ISA_AVAILABILITY;
Class super_class;
const char *name;
long version;
long info;
long instance_size;
struct objc_ivar_list *ivars;
struct objc_method_list **methodLists;
struct objc_cache *cache;
struct objc_protocol_list *protocols;
};该结构中,isa指向所属的Class,super_class指向父类别。在objc_runtime_new.h中,我们发现objc_class有如下定义:
struct object_class : objc_object
{
//Class ISA
Class superclass;
...
...
}什么是Meta Class
根据上面的描述,我们可以把Meta Class理解为一个Class对象的class。简单的说:
- 当我们发送一个消息给一个NSObject对象时,这条消息会在对象类的方法列表里查找。
- 当我们发送一个消息给一个类时,这条消息会在类的Meta Class的方法列表中查找。
而Meta Class也是一个Class,它跟其他Class一样有自己的isa和super_class指针。 具体的如图所示:
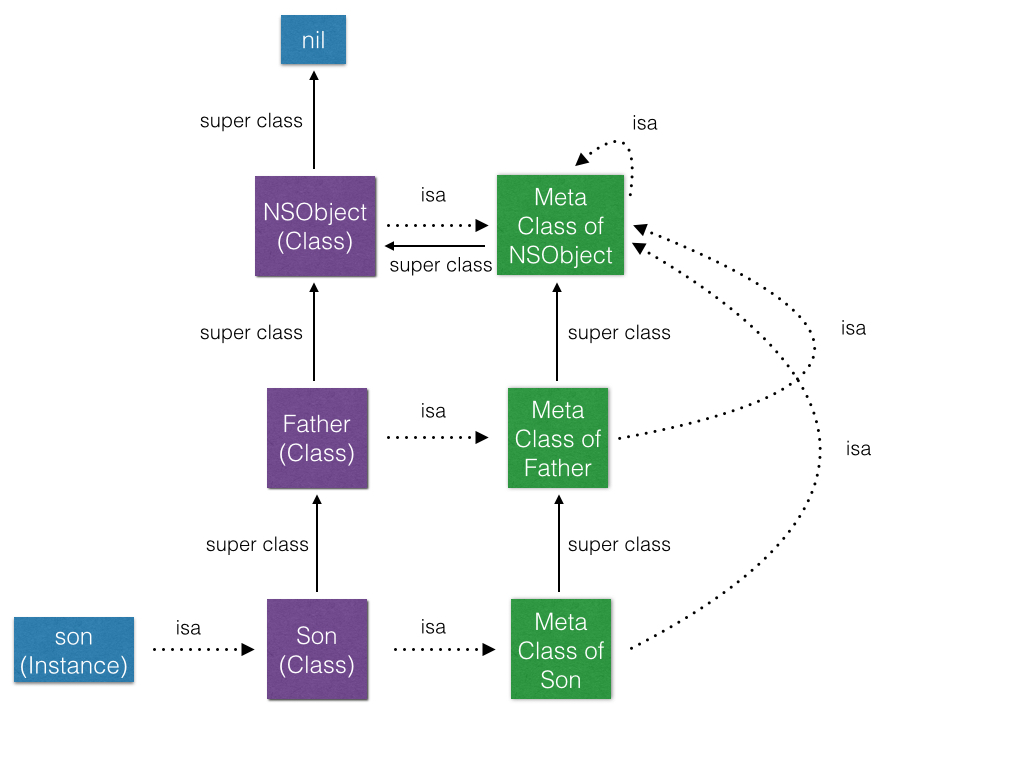
- 每个Class都有一个isa指针指向一个唯一的Meta Class
- 每一个Meta Class的isa指针都指向嘴上层的Meta Class
- 最上层的Meta Class的super class指向自己,形成一个环路
- 每一个Meta Class的super class指针指向它原本Class的 Super Class的Meta Class。但是最上层的Meta Class的 Super Class指向NSObject Class本身
- 最上层的NSObject Class的super Class指向nil。
华丽丽的分割线 其实上面说的根本没有卵用 我们来看看YYModel的序列化过程
序列化的步骤一般都是:
- 遍历类定义中的所有属性,储存在一个字典中。
- 找到所有属性对应的set和get方法,储存在一个字典里
- 确认json字典里的key和类定义中属性的映射关系,一般来说json字典里的key的名字就是我们类定义中的属性名,所以如果不需要定制化,这一步是可以省略的
- 解析需要序列化的字典,根据key和value的类型判断需要序列化的对象类型
- 根据该对象类型的属性和方法字典来实例化一个对象,并设置好值,这个就是我们要得结果了
YYModel的序列化过程也是这样,首先有一个YYClassInfo对象来储存class信息:
+ (instancetype)classInfoWithClass:(Class)cls {
if (!cls) return nil;
static CFMutableDictionaryRef classCache;
static CFMutableDictionaryRef metaCache;
static dispatch_once_t onceToken;
static OSSpinLock lock;
dispatch_once(&onceToken, ^{
classCache = CFDictionaryCreateMutable(CFAllocatorGetDefault(), 0, &kCFTypeDictionaryKeyCallBacks, &kCFTypeDictionaryValueCallBacks);
metaCache = CFDictionaryCreateMutable(CFAllocatorGetDefault(), 0, &kCFTypeDictionaryKeyCallBacks, &kCFTypeDictionaryValueCallBacks);
lock = OS_SPINLOCK_INIT;
});
OSSpinLockLock(&lock);
YYClassInfo *info = CFDictionaryGetValue(class_isMetaClass(cls) ? metaCache : classCache, (__bridge const void *)(cls));
if (info && info->_needUpdate) {
[info _update];
}
OSSpinLockUnlock(&lock);
if (!info) {
info = [[YYClassInfo alloc] initWithClass:cls];
if (info) {
OSSpinLockLock(&lock);
CFDictionarySetValue(info.isMeta ? metaCache : classCache, (__bridge const void *)(cls), (__bridge const void *)(info));
OSSpinLockUnlock(&lock);
}
}
return info;
}可以看到所有出现的class定义都会储存在一个全局静态字典classCache和metaCache中。我们再看一个YYClassInfo包含那些数据呢:
/**
Class information for a class.
*/
@interface YYClassInfo : NSObject
@property (nonatomic, assign, readonly) Class cls;
@property (nonatomic, strong, readonly) Class superCls;
@property (nonatomic, assign, readonly) Class metaCls;
@property (nonatomic, assign, readonly) BOOL isMeta;
@property (nonatomic, strong, readonly) NSString *name;
@property (nonatomic, strong, readonly) YYClassInfo *superClassInfo;
@property (nonatomic, strong, readonly) NSDictionary *ivarInfos; //< key:NSString(ivar), value:YYClassIvarInfo
@property (nonatomic, strong, readonly) NSDictionary *methodInfos; //< key:NSString(selector), value:YYClassMethodInfo
@property (nonatomic, strong, readonly) NSDictionary *propertyInfos; //< key:NSString(property), value:YYClassPropertyInfo
@end
/**
Instance variable information.
*/
@interface YYClassIvarInfo : NSObject
@property (nonatomic, assign, readonly) Ivar ivar;
@property (nonatomic, strong, readonly) NSString *name; //< Ivar's name
@property (nonatomic, assign, readonly) ptrdiff_t offset; //< Ivar's offset
@property (nonatomic, strong, readonly) NSString *typeEncoding; //< Ivar's type encoding
@property (nonatomic, assign, readonly) YYEncodingType type; //< Ivar's type
@end
/**
Method information.
*/
@interface YYClassMethodInfo : NSObject
@property (nonatomic, assign, readonly) Method method;
@property (nonatomic, strong, readonly) NSString *name; //< method name
@property (nonatomic, assign, readonly) SEL sel; //< method's selector
@property (nonatomic, assign, readonly) IMP imp; //< method's implementation
@property (nonatomic, strong, readonly) NSString *typeEncoding; //< method's parameter and return types
@property (nonatomic, strong, readonly) NSString *returnTypeEncoding; //< return value's type
@property (nonatomic, strong, readonly) NSArray *argumentTypeEncodings; //< array of arguments' type
@end
/**
Property information.
*/
@interface YYClassPropertyInfo : NSObject
@property (nonatomic, assign, readonly) objc_property_t property;
@property (nonatomic, strong, readonly) NSString *name; //< property's name
@property (nonatomic, assign, readonly) YYEncodingType type; //< property's type
@property (nonatomic, strong, readonly) NSString *typeEncoding; //< property's encoding value
@property (nonatomic, strong, readonly) NSString *ivarName; //< property's ivar name
@property (nonatomic, assign, readonly) Class cls; //< may be nil
@property (nonatomic, strong, readonly) NSString *getter; //< getter (nonnull)
@property (nonatomic, strong, readonly) NSString *setter; //< setter (nonnull)
@end我只截取了属性定义的部分。YYClassInfo储存了一个类里面所有的属性和方法字典,并保存了_cls、_superCls和_metaCls的签名。 主要使用了OC的class_copyMethodList、class_copyPropertyList和class_copyIvarList方法,动过cls签名获取了类的信息。 当然,说起来好像很简单,实际需要你对OC的底层非常了解,知道objc_method、objc_ivar和objc_property的定义,知道Type Encodings和Declared Properties这些信息,才能真的解析出我们需要的信息。 这里我找到了OC里面关于上面那些结构体的定义:
类的数据结构
Class(指针)
typedef struct objc_class *Class;
/*
这是由编译器为每个类产生的数据结构,这个结构定义了一个类.这个结构是通过编译器在执行时产生,在运行时发送消息时使用.因此,一些成员改变了类型.编译器产生"char* const"类型的字符串指针替代了下面的成员变量"super_class"
*/
struct objc_class {
struct objc_class* class_pointer; /* 指向元类的指针. */
struct objc_class* super_class; /* 指向父类的指针. 对于NSObject来说是NULL.*/
const char* name; /* 类的名称. */
long version; /* 未知. */
unsigned long info; /* 比特蒙板. 参考下面类的蒙板定义. */
long instance_size; /* 类的字节数.包含类的定义和所有父类的定义 */
#ifdef _WIN64
long pad;
#endif
struct objc_ivar_list* ivars; /* 指向类中定义的实例变量的列表结构. NULL代表没有实例变量.不包括父类的变量. */
struct objc_method_list* methods; /* 链接类中定义的实例方法. */
struct sarray * dtable; /* 指向实例方法分配表. */
struct objc_class* subclass_list; /* 父类列表 */
struct objc_class* sibling_class;
struct objc_protocol_list *protocols; /* 要实现的原型列表 */
void* gc_object_type;
};
Method(指针)
typedef struct objc_method *Method;
/* 编译器依据类中定义的方法为该类产生一个或更多这种这种结构.
一个类的实现可以分散在一个文件中不同部分,同时类别可以分散在不同的模块中.为了处理这个问题,使用一个单独的方法链表 */
struct objc_method
{
SEL method_name; /* 这个变量就是方法的名称.编译器使用在这里使用一个`char*`,当一个方法被注册,名称在运行时被使用真正的SEL替代 */
const char* method_types; /* 描述方法的参数列表. 在运行时注册选择器时使用.那时候方法名就会包含方法的参数列表.*/
IMP method_imp; /* 方法执行时候的地址. */
};
Ivar(指针)
typedef struct objc_ivar *Ivar;
/* 编译器依据类中定义的实例变量为该类产生一个或更多这种这种结构 */
struct objc_ivar
{
const char* ivar_name; /* 类中定义的变量名. */
const char* ivar_type; /* 描述变量的类型.调试时非常有用. */
int ivar_offset; /* 实例结构的基地址偏移字节 */
};
Category(指针)
typedef struct objc_category *Category;
/* 编译器为每个类别产生一个这样的结构.一个类可以具有多个类别同时既包括实例方法,也可以包括类方法*/
struct objc_category
{
const char* category_name; /* 类别名.定义在类别后面的括号内*/
const char* class_name; /* 类名 */
struct objc_method_list *instance_methods; /* 链接类中定义的实例方法. NULL表示没有实例方法. */
struct objc_method_list *class_methods; /* 链接类中定义的类方法. NULL表示没有类方法. */
struct objc_protocol_list *protocols; /* 遵循的协议表 */
};
objc_property_t
typedef struct objc_property *objc_property_t;
IMP
id (*IMP)(id, SEL, ...)
SEL
typedef struct objc_selector *SEL;
struct objc_selector
{
void *sel_id;
const char *sel_types;
};
objc_method_list
struct objc_method_list
{
struct objc_method_list* method_next; /* 这个变量用来链接另一个单独的方法链表 */
int method_count; /* 结构中定义的方法数量 */
struct objc_method method_list[1]; /* 可变长度的结构 */
};
objc_cache
struct objc_cache
{
unsigned int mask;
unsigned int occupied;
Method buckets[1];
};
objc_protocol_list
struct objc_protocol_list
{
struct objc_protocol_list *next;
size_t count;
struct objc_protocol *list[1];
};
实例的数据结构
id
typedef struct objc_object *id;
objc_object
struct objc_object
{
/* 类的指针是对象相关的类.如果是一个类对象, 这个指针指向元类.
Class isa;
};
objc_super
struct objc_super
{
id self; /* 消息的接受者 */
Class super_class; /* 接受者的父类 */
};有了上面这些信息相信所有人都知道作者的代码都在干嘛了,具体不表。反正到此为止,我们已经有了class的定义。 理论上下一步就可以解析了,但是作者额外多了一步,定制了映射关系。出现了一个新的class属性映射关系类的定义:
//A class info in object model.
@interface _YYModelMeta : NSObject {
@public
// Key:mapped key and key path, Value:_YYModelPropertyInfo.
NSDictionary *_mapper;
// Array<_YYModelPropertyInfo>, all property meta of this model.
NSArray *_allPropertyMetas;
// Array<_YYModelPropertyInfo>, property meta which is mapped to a key path.
NSArray *_keyPathPropertyMetas;
// The number of mapped key (and key path), same to _mapper.count.
NSUInteger _keyMappedCount;
// Model class type.
YYEncodingNSType _nsType;
BOOL _hasCustomTransformFromDictonary;
BOOL _hasCustomTransformToDictionary;
}
@end上面的YYClassInfo更像是一个抽象的模板,只是告诉我们类里面有这些属性和方法,没有告诉我们怎么去解析。_YYModelMeta这个类就是告诉我们怎么去解析的。 同样的所有_YYModelMeta都缓存在了一个全局静态字典里面。_YYModelMeta通过YYClassInfo的信息来实例化:
- (instancetype)initWithClass:(Class)cls {
YYClassInfo *classInfo = [YYClassInfo classInfoWithClass:cls];
if (!classInfo) return nil;
self = [super init];
// Get black list
NSSet *blacklist = nil;
if ([cls respondsToSelector:@selector(modelPropertyBlacklist)]) {
NSArray *properties = [(id<YYModel>)cls modelPropertyBlacklist];
if (properties) {
blacklist = [NSSet setWithArray:properties];
}
}
// Get white list
NSSet *whitelist = nil;
if ([cls respondsToSelector:@selector(modelPropertyWhitelist)]) {
NSArray *properties = [(id<YYModel>)cls modelPropertyWhitelist];
if (properties) {
whitelist = [NSSet setWithArray:properties];
}
}
// Get container property's generic class
NSDictionary *genericMapper = nil;
if ([cls respondsToSelector:@selector(modelContainerPropertyGenericClass)]) {
genericMapper = [(id<YYModel>)cls modelContainerPropertyGenericClass];
if (genericMapper) {
NSMutableDictionary *tmp = genericMapper.mutableCopy;
[genericMapper enumerateKeysAndObjectsUsingBlock:^(id key, id obj, BOOL *stop) {
if (![key isKindOfClass:[NSString class]]) return;
Class meta = object_getClass(obj);
if (!meta) return;
if (class_isMetaClass(meta)) {
tmp[key] = obj;
} else if ([obj isKindOfClass:[NSString class]]) {
Class cls = NSClassFromString(obj);
if (cls) {
tmp[key] = cls;
}
}
}];
genericMapper = tmp;
}
}
// Create all property metas.
NSMutableDictionary *allPropertyMetas = [NSMutableDictionary new];
YYClassInfo *curClassInfo = classInfo;
while (curClassInfo && curClassInfo.superCls != nil) { // recursive parse super class, but ignore root class (NSObject/NSProxy)
for (YYClassPropertyInfo *propertyInfo in curClassInfo.propertyInfos.allValues) {
if (!propertyInfo.name) continue;
if (blacklist && [blacklist containsObject:propertyInfo.name]) continue;
if (whitelist && ![whitelist containsObject:propertyInfo.name]) continue;
_YYModelPropertyMeta *meta = [_YYModelPropertyMeta metaWithClassInfo:classInfo
propertyInfo:propertyInfo
generic:genericMapper[propertyInfo.name]];
if (!meta || !meta->_name) continue;
if (!meta->_getter && !meta->_setter) continue;
if (allPropertyMetas[meta->_name]) continue;
allPropertyMetas[meta->_name] = meta;
}
curClassInfo = curClassInfo.superClassInfo;
}
if (allPropertyMetas.count) _allPropertyMetas = allPropertyMetas.allValues.copy;
// create mapper
NSMutableDictionary *mapper = [NSMutableDictionary new];
NSMutableArray *keyPathPropertyMetas = [NSMutableArray new];
if ([cls respondsToSelector:@selector(modelCustomPropertyMapper)]) {
NSDictionary *customMapper = [(id <YYModel>)cls modelCustomPropertyMapper];
[customMapper enumerateKeysAndObjectsUsingBlock:^(NSString *propertyName, NSString *mappedToKey, BOOL *stop) {
_YYModelPropertyMeta *propertyMeta = allPropertyMetas[propertyName];
if (propertyMeta) {
NSArray *keyPath = [mappedToKey componentsSeparatedByString:@"."];
propertyMeta->_mappedToKey = mappedToKey;
if (keyPath.count > 1) {
propertyMeta->_mappedToKeyPath = keyPath;
[keyPathPropertyMetas addObject:propertyMeta];
}
[allPropertyMetas removeObjectForKey:propertyName];
if (mapper[mappedToKey]) {
((_YYModelPropertyMeta *)mapper[mappedToKey])->_next = propertyMeta;
} else {
mapper[mappedToKey] = propertyMeta;
}
}
}];
}
[allPropertyMetas enumerateKeysAndObjectsUsingBlock:^(NSString *name, _YYModelPropertyMeta *propertyMeta, BOOL *stop) {
propertyMeta->_mappedToKey = name;
if (mapper[name]) {
((_YYModelPropertyMeta *)mapper[name])->_next = propertyMeta;
} else {
mapper[name] = propertyMeta;
}
}];
if (mapper.count) _mapper = mapper;
if(keyPathPropertyMetas) _keyPathPropertyMetas = keyPathPropertyMetas;
_keyMappedCount = _allPropertyMetas.count;
_nsType = YYClassGetNSType(cls);
_hasCustomTransformFromDictonary = ([cls instancesRespondToSelector:@selector(modelCustomTransformFromDictionary:)]);
_hasCustomTransformToDictionary = ([cls instancesRespondToSelector:@selector(modelCustomTransformToDictionary:)]);
return self;
}翻译成伪代码就是:
- 1.获取属性的白名单、黑名单和解析的key-value映射表。
- 2.根据这些信息生成Json字典里的key和类定义中的映射关系,保存在一个map中。
白名单的作用就是如果存在白名单则在实例化的时候只管白名单里面的属性,_YYModelMeta里面也只保存白名单里面的属性映射。黑名单的作用就是过滤掉黑名单里面的属性,其他的属性映射都保存。 当然一般简单地序列化是不需要这些个定制化的东西的,作者还额外实现了一些特殊属性的特殊映射关系,比如一些类定义里面的字典或者数组该如何实例化,我们就需要知道这些数组和字典里面储存的是 什么类型的value,作者通过modelContainerPropertyGenericClass这个接口,让用户自己来设置。作者还额外提供了一个接口modelCustomPropertyMapper,顾名思义,某些属性的名字跟 json字典中的key不一样或者本身就需要映射到跟属性不同名的key上,用户就可以通过这个接口返回一个字典来设置:
/**
Custom property mapper.
@discussion If the key in JSON/Dictionary does not match to the model's property name,
implements this method and returns the additional mapper.
Example:
json:
{
"n":"Harry Pottery",
"p": 256,
"ext" : {
"desc" : "A book written by J.K.Rowing."
}
}
model:
@interface YYBook : NSObject
@property NSString *name;
@property NSInteger page;
@property NSString *desc;
@end
@implementation YYBook
+ (NSDictionary *)modelCustomPropertyMapper {
return @{@"name" : @"n",
@"page" : @"p",
@"desc" : @"ext.desc"};
}
@end
@return A custom mapper for properties.
*/
+ (NSDictionary *)modelCustomPropertyMapper;在生成映射表的时候有个问题,那就是一个key只能对应一个value,加入类A中的属性B、C都要对应到json字典中的KeyB字段,则这个映射表是没办法实现的, 这也是为什么作者在_YYModelPropertyMeta的定义中添加_YYModelPropertyMeta *_next;这个属性。_YYModelPropertyMeta的完整定义如下:
// A property info in object model.
@interface _YYModelPropertyMeta : NSObject {
@public
NSString *_name; //< property's name
YYEncodingType _type; //< property's type
YYEncodingNSType _nsType; //< property's Foundation type
BOOL _isCNumber; //< is c number type
Class _cls; //< property's class, or nil
Class _genericCls; //< container's generic class, or nil if threr's no generic class
SEL _getter; //< getter, or nil if the instances cannot respond
SEL _setter; //< setter, or nil if the instances cannot respond
NSString *_mappedToKey; //< the key mapped to
NSArray *_mappedToKeyPath; //< the key path mapped to (nil if the name is not key path)
_YYModelPropertyMeta *_next; //< next meta if there are multiple properties mapped to the same key.
}
@end我们已经知道了YYClassInfo和_YYModelMeta的关系,那么_YYModelPropertyMeta和YYClassPropertyInfo是什么关系呢?我们看到YYClassPropertyInfo中 保存的是属性的原始模板信息,而且代码里有一段:
_YYModelPropertyMeta *meta = [_YYModelPropertyMeta metaWithClassInfo:classInfo
propertyInfo:propertyInfo
generic:genericMapper[propertyInfo.name]];可以看到_YYModelPropertyMeta是通过YYClassPropertyInfo模板生成的,_YYModelPropertyMeta里面保存的信息相对于YYClassPropertyInfo来说更少也更针对, _YYModelPropertyMeta把YYClassPropertyInfo中的get和set方法名转化成了SEL类型的对象,我学OC时间不长,也不知道该怎么称呼SEL对象,叫方法选择器?Whatever。。。 习惯了C++的朋友直接理解成函数地址也行,习惯了Window的消息分发机制的也可以理解为接受消息的对象,反正得到这个之后想要设置属性的值就只需要调用OC的发送消息接口就行了,比如下面的代码:
/**
Set number to property.
@discussion Caller should hold strong reference to the parameters before this function returns.
@param model Should not be nil.
@param num Can be nil.
@param meta Should not be nil, meta.isCNumber should be YES, meta.setter should not be nil.
*/
static force_inline void ModelSetNumberToProperty(__unsafe_unretained id model,
__unsafe_unretained NSNumber *num,
__unsafe_unretained _YYModelPropertyMeta *meta) {
switch (meta->_type & YYEncodingTypeMask) {
case YYEncodingTypeBool: {
((void (*)(id, SEL, bool))(void *) objc_msgSend)((id)model, meta->_setter, num.boolValue);
} break;
case YYEncodingTypeInt8: {
((void (*)(id, SEL, int8_t))(void *) objc_msgSend)((id)model, meta->_setter, (int8_t)num.charValue);
} break;
case YYEncodingTypeUInt8: {
((void (*)(id, SEL, uint8_t))(void *) objc_msgSend)((id)model, meta->_setter, (uint8_t)num.unsignedCharValue);
} break;
case YYEncodingTypeInt16: {
((void (*)(id, SEL, int16_t))(void *) objc_msgSend)((id)model, meta->_setter, (int16_t)num.shortValue);
} break;
case YYEncodingTypeUInt16: {
((void (*)(id, SEL, uint16_t))(void *) objc_msgSend)((id)model, meta->_setter, (uint16_t)num.unsignedShortValue);
} break;
case YYEncodingTypeInt32: {
((void (*)(id, SEL, int32_t))(void *) objc_msgSend)((id)model, meta->_setter, (int32_t)num.intValue);
}
case YYEncodingTypeUInt32: {
((void (*)(id, SEL, uint32_t))(void *) objc_msgSend)((id)model, meta->_setter, (uint32_t)num.unsignedIntValue);
} break;
case YYEncodingTypeInt64: {
((void (*)(id, SEL, int64_t))(void *) objc_msgSend)((id)model, meta->_setter, (int64_t)num.longLongValue);
}
case YYEncodingTypeUInt64: {
((void (*)(id, SEL, uint64_t))(void *) objc_msgSend)((id)model, meta->_setter, (uint64_t)num.unsignedLongLongValue);
} break;
case YYEncodingTypeFloat: {
float f = num.floatValue;
if (isnan(f) || isinf(f)) f = 0;
((void (*)(id, SEL, float))(void *) objc_msgSend)((id)model, meta->_setter, f);
} break;
case YYEncodingTypeDouble: {
double d = num.floatValue;
if (isnan(d) || isinf(d)) d = 0;
((void (*)(id, SEL, double))(void *) objc_msgSend)((id)model, meta->_setter, d);
} break;
case YYEncodingTypeLongDouble: {
double d = num.floatValue;
if (isnan(d) || isinf(d)) d = 0;
((void (*)(id, SEL, long double))(void *) objc_msgSend)((id)model, meta->_setter, (long double)d);
} break;
default: break;
}
}当然_YYModelPropertyMeta跟YYClassPropertyInfo的关系也是一个我们解析时使用的映射表,一个只是属性模板。 到这里我不产生了疑问:YYClassIvarInfo和YYClassMethodInfo对应的映射表呢?YYClassMethodInfo不需要映射,因为他不是属性,不需要赋值,但是YYClassIvarInfo 就不一样了,他表示一个实例变量。但是我们看作者的代码里前前后后好像就没YYClassIvarInfo的事儿。什么才是实例变量呢?一个类里面的实例变量是什么呢?不是属性么?一大串问号。。。。。 我们都知道OC的定义可以像下面这么写:
@interface A : NSObject{
NSString *_name;
}
@property (nonatomic, strong) NSString *name;
@end
@implementation A
@synthesize name = _name;
@end或者:
@interface A : NSObject{
NSString *name;
}
@property (nonatomic, strong) NSString *name;
@implementation A
@synthesize name;
@end或者
@interface A : NSObject
@property (nonatomic, strong) NSString *name;
@implementation A
@synthesize name;
@end区别是什么呢?看知乎大神的回答:
著作权归作者所有。 商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。 作者:RefuseBT 链接:http://www.zhihu.com/question/22195598/answer/39593235 来源:知乎
对于方式1,定义最完备。继承时,子类直接访问父类成员变量无需再@synthesize。缺点就是麻烦,重构也麻烦。第二种的问题,在于成员变量没有下划线。这个修改的好处你可能一开始体会不到。其实加下划线最大的好处在于局部变量命名不会冲突。比如你一个成员变量叫name,你的入参也叫name,就会出现覆盖。这个时候简便的办法是对name加冠词,比如aName、anObj,看起来还是挺恶心的。虽然OC也这样干。这个时候如果声明为_name就一劳永逸了,况且编译器还能替你做了这个事。第三种的问题,也是第一种的优势,就是你在父类中可以直接访问成员变量,但是子类中你无法访问,只能通过属性访问到。如果属性还是在.m中声明的,麻烦更多。另外从命名上还兼有第二种的缺陷。 那么最好的写法写法一: @interface Person : NSObject { } @property (nonatomic, strong) NSString *name; @end
@implementation Person @end 这个适用与一般情况,编译器自动生成成员变量_name,而且写法最简单,不必重复声明。写法二,针对继承情况下,向子类暴露父类成员变量:@interface Person : NSObject { NSString *_name; } @property (nonatomic, strong) NSString *name; @end
@implementation Person @synthesize name = _name; @end 其实@synthesize那条你不写也行,不过我还是喜欢声明完备,毕竟同一个成员变量,两个地方声明。
OK,这下我们知道了其实我们上面说的属性和实例变量基本就是一个东西了。但是我们一个属性对象YYClassPropertyInfo只是包含了get和set方法的名字以及属性名等一些基本信息。YYClassIvarInfo里面最特殊的就是@property (nonatomic, assign, readonly) ptrdiff_t offset; //< Ivar’s offset这个属性了。 学过C的都知道,所有数据的访问最后都是要转化为地址的,一个char[10]数组要访问第8个数据,就要知道第发布数据的地址,offset就相当于实例变量的地址索引。offset加上首地址就得到了实例变量的地址。但是我不得不说作者把这些数据保存下来之后貌似并没有使用。。。。。。
Anyway,我们已经得到了如何解析的映射表,愉快的进入了下一个步骤,解析Json数据。 作者在解析前加了很多道防线,防止用户传入的数据格式错误,不是一个字典或者jsonData类型的数据,这些这里就不表了。解析代码如下:
- (BOOL)yy_modelSetWithDictionary:(NSDictionary *)dic {
if (!dic || dic == (id)kCFNull) return NO;
if (![dic isKindOfClass:[NSDictionary class]]) return NO;
_YYModelMeta *modelMeta = [_YYModelMeta metaWithClass:object_getClass(self)];
if (modelMeta->_keyMappedCount == 0) return NO;
ModelSetContext context = {0};
context.modelMeta = (__bridge void *)(modelMeta);
context.model = (__bridge void *)(self);
context.dictionary = (__bridge void *)(dic);
if (modelMeta->_keyMappedCount >= CFDictionaryGetCount((CFDictionaryRef)dic)) {
CFDictionaryApplyFunction((CFDictionaryRef)dic, ModelSetWithDictionaryFunction, &context);
if (modelMeta->_keyPathPropertyMetas) {
CFArrayApplyFunction((CFArrayRef)modelMeta->_keyPathPropertyMetas,
CFRangeMake(0, CFArrayGetCount((CFArrayRef)modelMeta->_keyPathPropertyMetas)),
ModelSetWithPropertyMetaArrayFunction,
&context);
}
} else {
CFArrayApplyFunction((CFArrayRef)modelMeta->_allPropertyMetas,
CFRangeMake(0, modelMeta->_keyMappedCount),
ModelSetWithPropertyMetaArrayFunction,
&context);
}
if (modelMeta->_hasCustomTransformFromDictonary) {
return [((id<YYModel>)self) modelCustomTransformFromDictionary:dic];
}
return YES;
}很简单,如果我们的映射表中的key超过了提供的json字典中的key的个数,我们就认为有些字段是不要设置值的,所以对json字典进行遍历,反之就对映射表进行遍历。 最后如果我们有一些自定义的转化规则,在最后调用用户自己写的modelCustomTransformFromDictionary方法。至此YYModel的解析就结束了
总结
YYModel的作者真的是一个大神,我真心佩服这样的一个90后(同为90的我惭愧不已),他写了很多开源的第三方库,而这些第三方库都是他在这两年内通公司项目总结等归纳出来的, 其中有很多很强大的YYText等控件(解决了文字竖排的问题,也是我下一个要学习的库)也得到了很多人的关注。其中YYModel只是这位大神利用业余时间2周写出来的随笔。。。。我 花了近1一个月时间才勉强弄懂了七八分,要让我自己写那是万万不能的。一个阶段的学习计划应该是先把YYModel再重新吃一边,直到吃透了,然后花两周时间默写出来。。。 然后在学习大神的YYText库,丰富我之前写的可怜的CoreText库(相比之下我这个简直不能叫库)。。。。。